Running Marimo with uv¶
You can run a Marimo notebook using uv through one of the following methods:
Within a project environment
Temporary installation (cached)
Directly from a URL
Using
uvas a globally installed tool
Running in a Project Environment¶
We recommend running Marimo within a project-specific environment.
Here’s how you can set it up:
uv venv
uv pip install marimo
uv run marimo edit hi.py
The uv run command provides the simplest way to access the virtual environment.
However, if you prefer to activate it manually, you can do so with the following commands:
source .venv/bin/activate
marimo edit hi.py
Using Specific Python Versions¶
To specify a Python version, add the --python option while creating the venv. For example:
uv venv --python 3.13
Tip
uv will automatically fetch Python versions as needed — you don’t need to install Python to get started.
If no version is specified, the default Python version is used (currently: [TODO: Specify default Python version]).
Installing Packages¶
There are three ways to install additional packages:
Via Terminal
Run the following command:uv pip install matplotlib polars
Within the Notebook
Typeimport polars as pd. Run the cell, and a “Missing package” pop up window will appear.
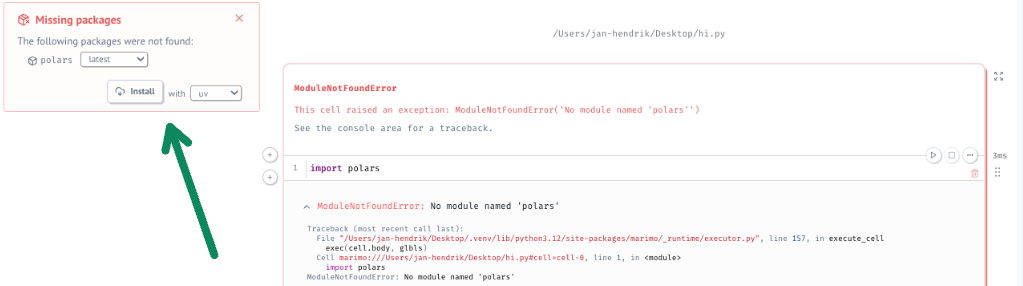
Using the Packages Tab
Navigate to the “Packages” tab and select the desired package.
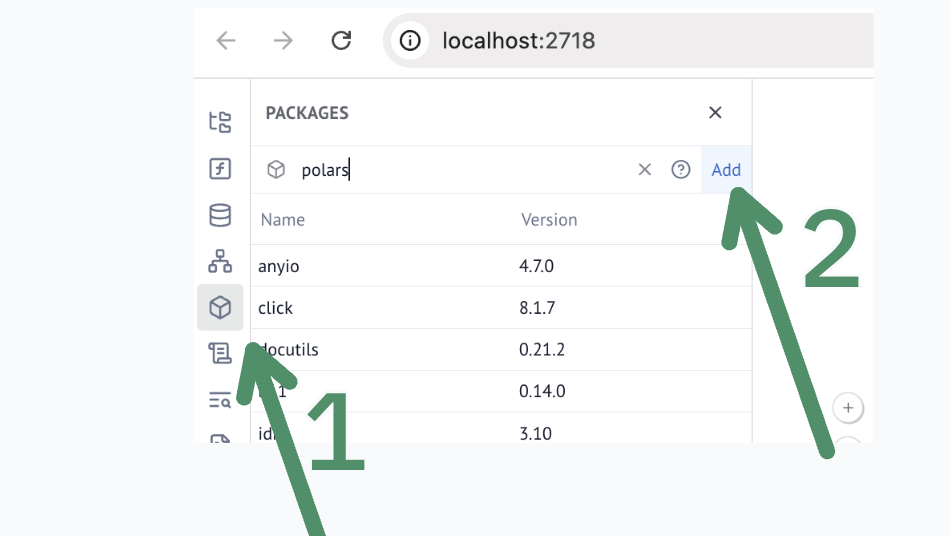
Defining Dependencies with pyproject.toml¶
A pyproject.toml file makes it easier to manage your project’s dependencies in one place. Using the uv tool, you can quickly set up and customize your project’s environment
uv init # Creates a pyproject.toml file
uv add marimo # Adds "marimo>=0.9.31" to dependencies
uv run marimo edit hi.py
Reading a pyproject.toml from an Existing Project¶
If you already have a pyproject.toml file—for example, when cloning an existing project—you can use the uv sync command to synchronize and install the dependencies defined within it:
uv sync
uv run marimo edit hi.py
This command ensures that your environment matches the dependency specifications of the existing project, making it simple to get up and running without manually adding packages.
Temporary Installation¶
When you run a command with uv tool run, no virtual environment folder is created in your working directory. Instead, uv will:
Cache the dependencies or re-use already cached ones that are specified.
Create a temporary virtual environment on your system.
Remove the temporary environment as soon as the process exits.
This lightweight approach keeps your workspace clean while still providing an isolated, dependency-managed environment for running commands.
For example, you can run:
uv tool run marimo edit hi.py
To specify additional requirements, enable the --sandbox mode by running:
uv tool run marimo edit hi.py --sandbox
While in the notebook, you can install packages as shown earlier, either using the pop-ups or through the packages tab. However, note that adding packages via the terminal is not supported in this mode. #TODO: fact check this.
And the special thing: The notebook is now fully self-contained and can be reproduced by anyone. THis is because the following package metadata was added to the notebook according to (PEP 723 – Inline script metadata)[https://peps.python.org/pep-0723/]
# /// script
# requires-python = ">=3.11"
# dependencies = [
# "polars==1.16.0",
# ]
# ///
uvx marimo edit hi.py
Here, uvx is simply an alias for uv tool run.
From URL¶
This pattern will run marimo from a URL.
With uv run URL
What is the word
I’m looking for a word to describe this kind of code pattern. `pip install I can run a script like this uv run https://gist.githubusercontent.com/kolibril13/f4597c16452b4b72965c8d20fe6c0978/raw/a7757d3f206d467f6e76eeea621e64b0cb92530c/benchmark.py
# globally installed tool
This is not recommended, as dependencies will be installed globally as well. #TODO:FactCheck
uv tool install marimo
Use a **specific python version** (this will overwrite the previous global installation):
UV_PYTHON=python3.11 uv tool install marimo
**Update** global version of marimo:
uv tool install marimo –upgrade.
**Uninstall**
uv tool install marimo